#RetailTech #customerengagement @facenote #facerecognition #bebetter #sellmore #happycustomers #smile4melissa #melissashoes
Barney Stacher - Business, Brand, Sales & Marketing Development
Things that make me go, "hmmmm!?".
Thursday, January 25, 2018
Thursday, December 28, 2017
Tuesday, December 12, 2017
A New/Old Tool for Personal and Business InSight
Tarot is a reflective tool for knowing and understanding...
Tarot can provide you In:Sight into yourself, your relationships, your business.
Think of Tarot as a reflective tool, like a session with a heart-centered counselor to guide you on the journey of discovery... like a priest, rabbi, therapist, coach.
You have the answers and Tarot will help you uncover them.
Gayle Stacher
Monday, October 9, 2017
What is Your (Business) Learning Style?
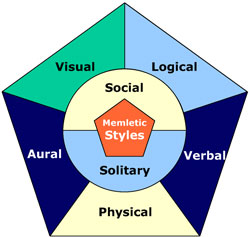
"Research shows us that each learning style uses different parts of the brain. By involving more of the brain during learning, we remember more of what we learn."
The same principles apply to educating employees, clients, vendors, and prospects. Messages repeated and reinforced in multiple learning modes are more likely to be absorbed and internalized.
Communicate to the needs of the audience.
If you are curious about your learning style: https://goo.gl/zfXG6vCommunicate to the needs of the audience.
#businesslearning #learningstyle #learningreinforcement
#consistency #onmessage #rinseandrepeat
Wednesday, May 31, 2017
Intuition is at the intersection of knowledge, experience and intelligence.
Heuristic v. Algorithmic
Heuristic, in a nutshell is an "Educated guess". Wikipedia explains it nicely. At the end, a "general acceptance" method is taken as an optimal solution to the specified problem.
Heuristic is an adjective for experience-based techniques that help in problem solving, learning and discovery. A heuristic method is used to rapidly come to a solution that is hoped to be close to the best possible answer, or 'optimal solution'. Heuristics are "rules of thumb", educated guesses, intuitive judgments or simply common sense. A heuristic is a general way of solving a problem. Heuristics as a noun is another name for heuristic methods.
In more precise terms, heuristics stand for strategies using readily accessible, though loosely applicable, information to control problem solving in human beings and machines.
While an algorithm is a method containing finite set of instructions used to solving a problem. The method has been proven mathematically or scientifically to work for the problem. There are formal methods and proofs.
Heuristic algorithm is an algorithm that is able to produce an acceptable solution to a problem in many practical scenarios, in the fashion of a general heuristic, but for which there is no formal proof of its correctness.
Cognitive Bias
There exists potential for cognitive biases in using heuristics in judgment and decision making, including:
- Availability heuristic – estimating what is more likely by what is more available in memory, which is biased toward vivid, unusual, or emotionally charged examples.
- Representativeness heuristic – judging probabilities on the basis of resemblance.
- Affect heuristic – basing a decision on an emotional reaction rather than a calculation of risks and benefits.
Thursday, March 16, 2017
Become an Expert Sales Manager... in 28 not so simple steps.
BUSINESS TO BUSINESS SELLING
COURSE OUTLINE
· This course is designed for owners and executives of consumer product companies seeking to increase their Business-to-Business sales effectiveness.
· On completion of this course participants will have a better ability to sell their product, manage accounts, internal sales people and sales representatives, and implement a more effective B2B revenue growth strategy.
|
1) Sales Psychology
|
a) The Professional Salesperson is a Business Consultant
|
b) Sales as a Profession
|
c) Seller-Buyer Equation
|
d) The Sales Personality
|
e) Eight Roles for Sales Professional to excel in B2B Sales
|
2) Buying Psychology
|
a) Buyer Profiling
|
b) Buying Influences
|
c) Buyer fears & Risks
|
d) Buyer expectations
|
3) Strategic Sales Planning
|
a) Define USPs & Value Proposition
i) What is the compelling story?
|
b) Identifying Market Segments & Market Potential
|
c) Competitive Analysis - SWOT
|
d) Setting Sales Goals - Month/Quarter/Annual
|
4) Tactical Sales Planning
|
a) Prioritizing Markets & Products
|
b) Identify highest potential Accounts/markets
|
c) Set call priorities and frequencies
|
d) Breaking monthly goals into daily action items
|
e) Developing a prospect call schedule for maintaining healthy Pipeline
|
5) Territory and Channel Planning
|
a) How to organize your sales territory to maximize productivity
b) Selling into multiple market channels and retailer types
|
c) Product/market Mapping
|
d) Manage/Travel the territory in most time efficient manner
|
6) Time Management
|
a) Optimal use of golden hours of selling
|
b) Differentiate selling from non-selling activities
|
c) Reducing Interruptions
|
d) Quantify value of time
|
e) Inbox Management
|
f) "ROE" Gap Analysis
|
7) Prospecting
|
a) Sales prospecting fundamentals
|
b) Create Prospect Profile to identify most profitable customers
|
c) Active Prospecting - Identify resources to Locate Ideal Prospects
|
d) Passive Prospecting - Lead generation methods
|
e) Tactics to identify and reach medium-to-high level decision makers
|
f) Prospecting best practices for improving prospect quality
|
g) Pre-Qualifying a Lead
|
8) Pre-Call Planning & Research
|
a) Customer Profiling - Organizational & Individual
|
b) Identifying power people within the buying organization
|
c) Identify the six decision-making roles involved in B2B sales
|
d) Understanding buying process, buying influences & buyer personalities & fears
|
e) Developing a Prospect Specific Value Proposition
|
f) Pre-Planned Script - Anticipating conversations
|
g) The four essential objectives for every sales call
|
h) How to plan and prepare for every sales call
|
9) Relationship Selling
|
a) Understanding business relationships.
|
b) Components of a positive business relationship.
|
c) Analyze & assess relationships with every key person in your territory.
|
d) How to assess a customer’s personality style quickly and accurately.
|
e) Improving your relationships by adjusting style
|
10) Communication Skills and the Sales Conversations
|
a) Types of communication - verbal and nonverbal
|
b) E-Mail Communication
|
c) Recognizing positive & negative signs in other people & how to communicate more effectively.
|
d) Identifying communication & personality tendencies
|
e) Understanding your own personality tendency
|
f) f. Adjusting communication style to suit people of different personalities.
|
i) How to phrase questions
|
ii) How to present ideas
|
iii) How to respond to questions & concerns
|
g) Persuasive communication
i) Vocabulary and semantics which impact action
ii) Assumptive v. Asking
|
h) Listening Skills
|
11) Competitive Analysis & Strategy
|
a) Competitor to Product/service Matrix
|
b) Competitor Analysis Quadrants
|
c) Objections Quadrant
|
d) Neutralize, Prevent and/or Respond to Competitor Created objections
|
e) Competitor's Weaknesses
|
f) Unique and Distinctive Selling Points
|
g) Creating Objections for Your Competitors
|
12) Trade Show Sales and Trade Marketing
a) Selecting the right show(s) and location
b) Setting a budget and measurable and achievable objectives
c) Designing a stand that attracts customers and helps sells your product
d) Pre-show marketing and opportunities to stand out during the show
e) Utilizing sales agencies to build show effectiveness
f) Effective sales materials, merchandising and promotions
g) Engaging trade press to maximize exposure
13) Integrating Wholesale into Website/Online Presence
a) Tools to save time, pre-qualify prospects and increase sales conversion
b) Building retailer and consumer awareness
c) Providing information of value to prospects
d) Communicating experience and feeling to the retailer and their customer
14) Independent Sales Representation
a) When to hire, when to fire
b) Sourcing and qualifying
c) Training and managing
d) Standard procedures and rules of engagement
i) Commissions and payment terms
ii) Showrooms, trade-shows, samples and support materials
iii) Key account sales
iv) Benchmarks and goals
e) When to expand your internal team
i) Sales management
ii) Telemarketing
15) Preparing your staff to sell – Cold-Calling (Telephone)
a) Using a warm-up call or email
|
b) Cold-Calling as a process to systematically qualify a prospect.
|
c) Opening a Sales Call - Build Rapport within first few moments
|
d) Cold Calling Etiquettes & Ethics
|
e) Planning & Setting Call objectives
|
f) Overcoming Call reluctance or Fear of cold calling
|
g) Getting Past the Gatekeepers
|
h) Communicating with top-level executives
|
i) Strategically manage initial contact objections over the telephone
|
j) Securing Appointments
|
k) Acquiring agreement for customer actions
|
l) Turning incoming calls into sales
|
16) Pre-appointment Planning
|
a) Communicating the Agenda
|
b) Sending across information in Advance
|
c) Re-Confirming the appointment
|
d) Preparing self
|
17) Sales Appointments
|
a) Maintaining Professional Appearance & Body Language
|
b) Opening a Sales Call - Build Rapport within first few moments
|
c) Judging Customer’s State of Mind & adjusting accordingly
|
d) Setting the meeting agenda & objectives
|
e) The interim close - Acquiring agreement for customer actions
|
f) Defining Purpose, Agenda, Action Items & perceived outcomes next steps
|
i) Follow-Up Meeting
|
ii) Product Demo / Sales Presentation
|
iii) Product Test or Pilot Program
|
iv) Proposal Submission
|
g) Convert screeners and gatekeepers into coaches
|
18) Asking Questions
|
a) Asking questions in a Conversational manner (as opposed to being Interrogative)
|
b) Etiquettes while asking questions
|
c) Three question-asking strategies to confidently handle any situation.
|
d) Getting a customer to share deep & important information with you.
|
e) How to effectively use open vs. close-ended questions.
|
f) WIN Analysis - using questions to uncover true Wants, Issues & Needs
|
g) Asking Questions to
|
i) Develop future/latent Needs
|
ii) Understanding the buying Process
|
iii) Identifying all decision makers
|
iv) Classifying decision makers as - Gatekeeper, Integrator, Virtual Authority, User, Power Broker
|
v) Identify other buying influences
|
h) Preparing powerful questions
|
19) Proposing a Solution
|
a) Quickly identify needs only you can fill
|
b) Proposing a Solution with Benefit Statements
c) Strategically position yourself as a partner to your prospects
|
d) Lead the prospect to rule-out the competition by setting the buying criteria around your USPs.
|
20) Responding to Questions/concerns
|
a) Handling questions/requests for Price & Proposals
b) Why is it good when they ask for a discount
|
c) Eliminating Doubts
|
d) Handling an irate, rude or threatening customer
|
21) Overcoming Objections
|
a) Exploring and expecting Objections
|
b) Responding to the most Common Objections
|
c) Objection Prevention, Acknowledgement and Diffusion Strategies
|
22) Product DEMOs & Sales Presentations
|
a) Preparing a Presentation
|
b) Organizing & Logistics of a presentation
|
c) Presentation tactics to present persuasively.
|
d) Public Speaking and Selling Skills
|
i) Confident Public Speaking and Overcoming Fear
ii) Opening & closing
|
iii) Keeping them alive & interested
|
iv) Presentation Etiquettes
v) Managing time
|
vi) Using Q&A to enhance your credibility
|
e) Steps in answering Qs
|
i) Verify that you understand the question
|
ii) Clarify the intent of the question
|
iii) Answer the question with right amount of information
|
iv) Confirming if their question was answered
|
f) Most common questions that you will face and knock-out answers
|
g) Handling Hostile & Competitive Questions
|
h) Dealing with hostile or disinterested audiences
|
i) Common demo mistakes and how to avoid them.
|
j) Handling Product Crashes and Bugs
|
k) Dealing with objections during a demo/presentation
|
l) Establishing credibility with technical audiences
|
m) Establishing credibility with C-Level and executive audiences
|
23) Writing a Proposal which stands out from your competitors’
a) Visual cues
b) Establishing credibility and trust
c) Solution Driven
d) Actionable information
|
24) Follow-Ups
|
a) Staying in control by knowing where each of your priority prospects are in the sales process
|
b) Anticipate & block competitor advances
|
c) How to advance the buying process
|
d) How to shorten the sales cycle
|
25) Negotiating
|
a) Seven step process to Guided Negotiations
|
b) Avoiding Discounts or Using Them as a Sales Tool
|
c) Gaining commitments
|
d) Adversarial v. Principled Negotiations
|
e) Ways to counter adversarial tactics
|
f) Means to Establish Power
|
g) Understanding "Needs, Interests, Wants" model to develop negotiation strategies
|
26) Closing
|
a) When to & when not to Close
|
b) Closing techniques
|
i) A few comfortable closes
|
ii) How to create an urgency
|
27) Pipeline Management
|
a) Calculate a more accurate pipeline
|
b) Updating & renewing the pipeline
|
c) Action-plan for top prospects for things to be done in order to close
|
d) Analyzing Lost Sales - Identifying strategy & timeline to win them back
|
28) Post Sales
|
a) On-Boarding
|
b) Referrals & testimonials
|
c) Repeat business
|
d) Up-Selling
|
e) Cross-Selling
f) Building Loyalty
g) Creating Spokespeople
|
-->
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)


